Definition:
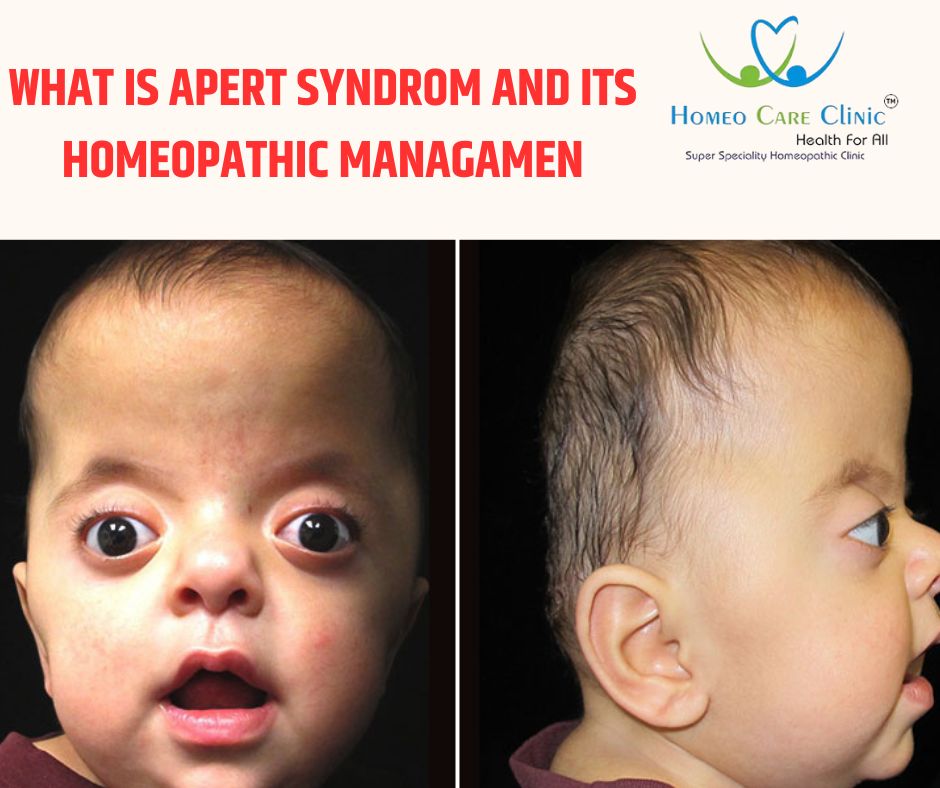
Apert syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by abnormalities in the skull, face, hands, and feet. It results from mutations in the FGFR2 gene, leading to premature fusion of certain skull bones and affecting the development of other structures. Individuals with Apert syndrome may have distinctive facial features, syndactyly (fusion of fingers and toes), and other associated health issues. Early intervention and multidisciplinary care are often necessary to address the diverse challenges associated with this condition.
Cause of apert syndrome:
Apert syndrome is primarily caused by mutations in the FGFR2 (fibroblast growth factor receptor 2) gene, located on chromosome 10. These mutations are typically point mutations, where a single nucleotide is changed in the DNA sequence of the gene. The specific mutations associated with Apert syndrome lead to the activation of the FGFR2 protein, disrupting normal signalling pathways involved in cell growth and development.
The FGFR2 protein is a receptor that plays a crucial role in regulating cell division, growth, and differentiation, particularly in the development of bones and connective tissues. The mutated FGFR2 gene in Apert syndrome leads to increased activity of the protein, causing premature fusion of certain skull bones during fetal development. This premature fusion, known as craniosynostosis, affects the shape of the head and face, leading to the characteristic features of Apert syndrome.
In addition to craniosynostosis, individuals with Apert syndrome often exhibit syndactyly, where fingers and toes are fused together. Other abnormalities in the hands and feet may also be present. The specific nature and severity of the features can vary among affected individuals.
It’s important to note that most cases of Apert syndrome occur sporadically, meaning they are not inherited from parents. The mutations in the FGFR2 gene typically arise as new mutations during the formation of the egg or sperm or shortly after fertilization. While the exact mechanisms leading to these mutations are not fully understood, advanced paternal age has been associated with an increased risk of having a child with Apert syndrome.
Types of Apert syndrome:
There is generally one recognized type of Apert syndrome, but the severity and specific manifestations of the condition can vary among individuals. The variations are often related to the specific FGFR2 gene mutations and other genetic and environmental factors. While there is a common set of characteristics associated with Apert syndrome, the extent and combination of features can differ.
The primary features of Apert syndrome include craniosynostosis (premature fusion of certain skull bones), distinctive facial features, and syndactyly (fusion of fingers and toes). The severity of these features can vary, and individuals with Apert syndrome may also experience other associated health issues such as hearing loss, intellectual disability, and abnormalities in other organs.
It’s important to note that while there may be variations in the severity and specific features, the underlying cause of Apert syndrome remains the same—a mutation in the FGFR2 gene. The variations in the clinical presentation of Apert syndrome are more individual differences rather than distinct types of the syndrome.
Signs and symptoms of Apert syndrome:
- Craniosynostosis: Premature fusion of skull bones leading to an abnormally shaped head and face
- Facial abnormalities: Distinctive facial features such as a high forehead, a beaked nose, and shallow eye sockets.
- Syndactyly: Fusion of fingers and toes, often giving the hands and feet a distinctive appearance.
- Other limb abnormalities: Apart from syndactyly, individuals may have additional hand and foot anomalies.
- Intellectual disability: Some individuals with Apert syndrome may experience intellectual challenges, although the degree can vary.
- Hearing loss: Conductive hearing loss due to abnormalities in the middle ear is common.
- Dental issues: Crowded or misaligned teeth may be present.
- Respiratory problems: Due to abnormalities in the skull and facial structure, individuals may experience respiratory issues.
Homeopathic Approach:
Homeopathic today is rapidly growing system and is being practiced all over the world Its strength lies in its evident effectiveness as it takes a holistic approach towards the sick individuals through promotion of inner balance at mental, emotional, spiritual and physical level. When is concerned there are many effective medicines available in homeopathy, but the selection depends upon the individuality of patient mental and physical symptom.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Homeo Care Clinic offers a holistic approach to treating Apert syndrome. These medicines mention above can treat the underlying causes of the condition and offer relief from the discomfort. However, it is important to consult a qualified practitioner for the correct dosage and duration of treatment. Dr Vaseem Chaudhary, Homeo Care Clinic Provides comprehensive care for various ailments, including Apert syndrome, and offers customized treatment plans on individual requirements.